

It is an Internet protocol that defines how a client machine can connect to a server via a proxy. When a server connects to this port, it is forwarded to the remote machine, then it is forwarded to the dynamic machine on a dynamic port. It creates a socket on the local machine that works as a SOCKS proxy server or you can say It sets up your local machine as a SOCKS proxy server and by default, it listens on port 1080. Local and Remote Port forwarding allows you to tunnel and communicates with a single port but in Dynamic Port forwarding you can runnel and communicate with a range of ports. The third and the last type of port forwarding is Dynamic Port Forwarding. Remote port forwarding is mainly used to give access to someone from the outside to an internal service. Or, you can use the following command to forward port 5000 on the remote machine to port 3000 on the local machine. The SSH server will listen on port 8080 and will tunnel all traffic from 8080 to port 3000 on your local machine
DESTINATION:DESTINATION_PORT – The Port and IP address or hostname of the destination machine.Any port number greater than 1024 can be used. LOCAL_PORT – The port number and IP address of the local machine.

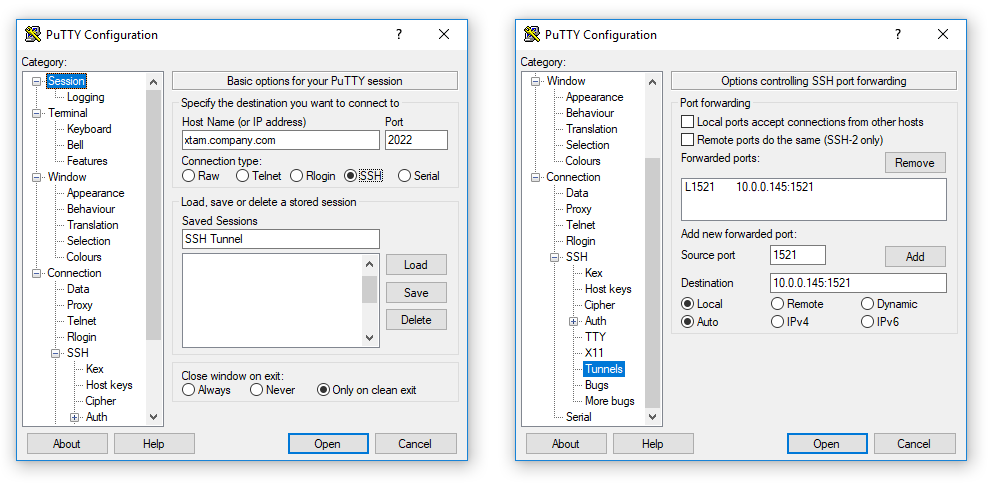
Or ssh -L LOCAL_PORT:DESTINATION:DESTINATION_PORT ]SSH_SERVER The -L is used to configure Local port forwarding ssh -L 8080::3000 Let’s take an example that you are restricted by a firewall to access an application running on a remote server on port 3000. It is also used for remote file share over the internet and through jump servers. It is mainly used to connect to a remote service on an internal network from the outside like a database. And then the server connects to a different destination machine on the configured port. SSH Client checks for the connection on a specific given port and when it receives a connection request, it tunnels the connection to a specific port on a remote SSH server. Local forwarding is the practice of forwarding a port from the client machine(Local SSH Client) to the remote machine(SSH Server) and then the connection is forwarded to another port of the destination machine. SSH Tunneling is also known as SSH Forwarding and it is an easy and effective way of transporting data that use an encrypted protocol(FTP), bypassing firewalls and accessing geographically restricted content. Apart from the file transmission, SSH Tunneling can also be used to access intranet services across firewalls and to implement VPN. Simply, you can say that it is a tunnel to transfer data from one place to another in a secure way. SSH Tunneling is the way of transmitting unencrypted traffic or data through an encrypted channel.
UNIX SSH TUNNEL HOW TO
In our today’s article, we will see how to set up SSH Tunneling and route your traffic securely via SSH tunnels. SSH Tunneling is a practice of creating a secured and encrypted SSH connection between a server machine and a client machine through which data can be transferred and service can be relayed.
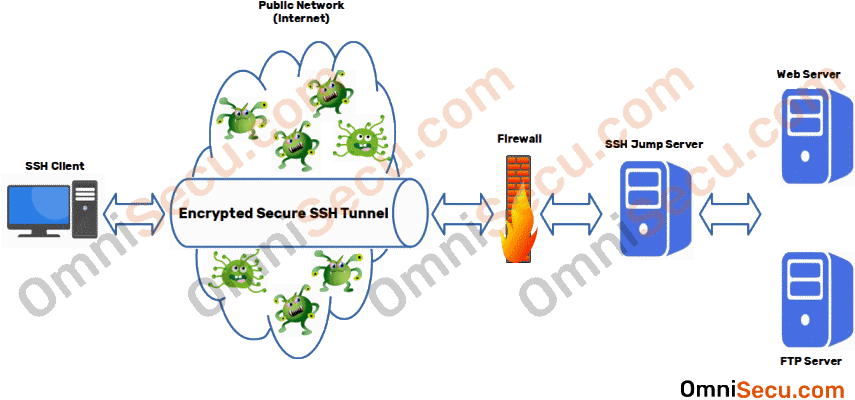
Therefore, SSH Tunneling is used to transmit data in a fast and secured manner from source to client machine and vice versa. If you are connecting with a different Linux device on a different network then you would have to expose it to the public internet and that may put your system and files at the risk.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
